
User and nouser These are very useful options. With noauto, the device can be mounted only explicitly. If you don't want the device to be mounted automatically, use the noauto option in /etc/fstab. For more information,Īuto and noauto With the auto option, the device will be mounted automatically (at bootup, just like I told you a bit earlier, or when you issue the mount -a command). Take a look at the most widely used ones only. Yes, there are many options available, but I'll This is also the most confusing column in the fstabįile, but knowing what some of the most common options mean, saves youįrom a big headache. The fourth column in fstab lists all the mount options for the device or partition. That's why it's wise to let the systemĪutomatically detect the filesystem type of media such as floppies and
#Fstab defaults windows
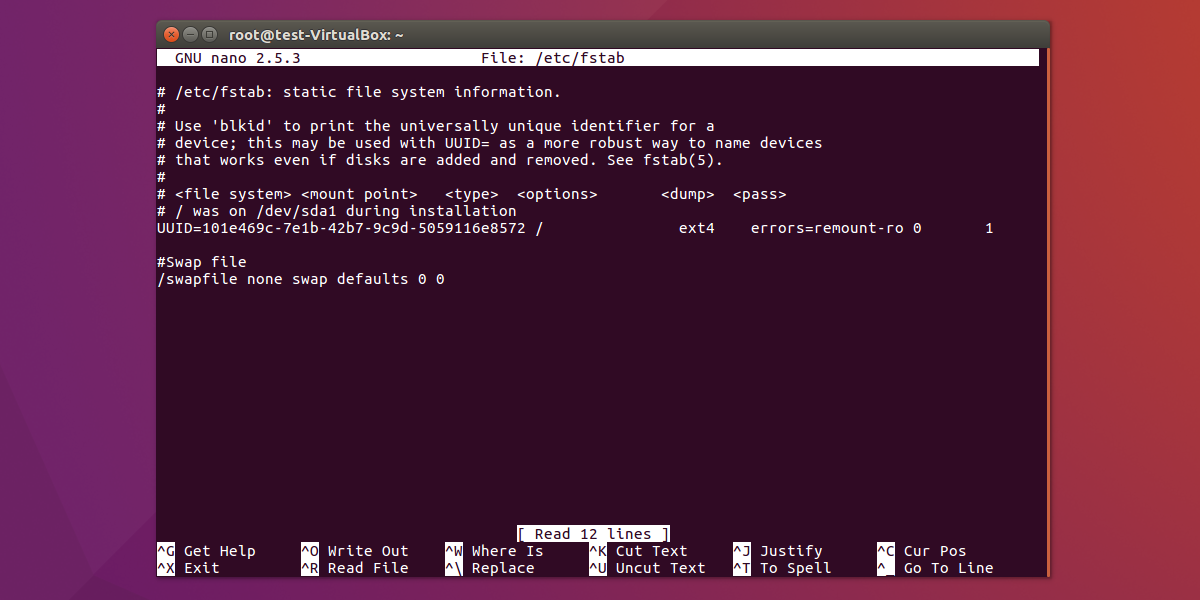
One floppy might be formatted for Windows and If you take a lookĪt the example fstab above, you'll see that the floppyĪnd CD-ROM both have "auto" as their filesystem type. That the filesystem type is detected automatically. No, this isn't a filesystem type :-) The option "auto" simply means Writing to NTFS partitions is a bit shabby at this moment. Linux, I suggest formatting them as Vfat, because Linux's support for If you want to be able to write to your Windows partitions from In 2000 and XP you can choose theįilesystem type, so 2000 and XP partitions may be formatted as Vfat, (95, 98, ME) all use Vfat (more widely known as FAT32), and the NT Your Windows partitions are probably either Vfat or NTFS. The filesystem type "swap" is used in your swap partitions. Swap The filesystem name is self-explanatory. ReiserFS as their default filesystem for Linux partitions. Many Linux distros (including SuSE) have started using LikeĮxt3, ReiserFS is a journaled filesystem, but it's much more advanced Your Linux partitions may very well be formatted as ReiserFS. Meaning that if you turn the computer off without properly shuttingĭown, you shouldn't lose any data and your system shouldn't spend agesĭoing filesystem checks the next time you boot up. Is a newer filesystem type that differs from Ext2 in that it's journaled, Usually the default filesystems for almost every new Linux distro. Standard filesystem for Linux, but these days, Ext3 and ReiserFS are Very likely your Linux partitions are Ext3. Manyĭifferent filesystems are supported but we'll take a look at the most Specifies the filesystem type of the device or partition.

Mount /dev/hda2 and /dev/hdb1? By looking at the /etc/fstab file of course. If / wasn't mounted! But how does the system know where you want to
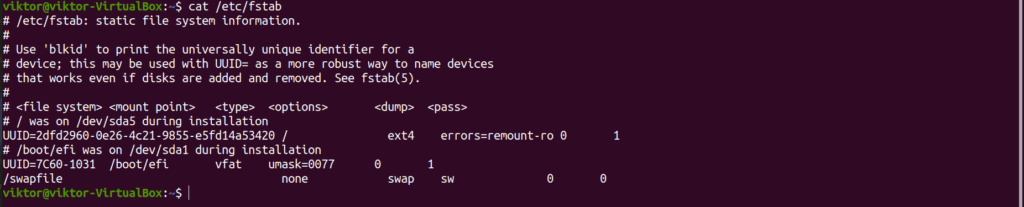
Wouldn't, you'd have a hard time using your cool Linux system becauseĪll the programs you use are in / and you wouldn't be able to run them This is done automatically when your Linux system boots up. There are lines that look like this:Īs you've learned, these lines mean that /dev/hda2 will be mounted to / and /dev/hdb1 to /home. For example, have a look at the example fstab above. If it doesn't, simply create it.Īnd devices are also automatically mounted when your Linux system boots Just make sure the mount point is a directory that already exists on If you're not satisfied with the defaults your distro has given you. You can freely change the default mount points listed in /etc/fstab If there is no entry for /dev/fd0 in my fstab when I issue the command above, mount gets very confused because it doesn't know where to mount the floppy. my floppy will be mounted in /media/floppy, because that's the default mount point specified in /etc/fstab. What does all this mean? If I type the following command: As you probably noticed when looking at the example fstab, I use SuSE's mount points as an example.

Most distros create them under /mnt, but some (at least SuSE) under /media. Like you already learned from the Mounting tuXfile, most Linux distros create special directories for mount points. That is the directory where the device willīe mounted if you don't specify any other mount point when mounting the The mount point specified for a device in /etc/fstab When you mount stuff manually: what is the device or partition, and They tell the mount command exactly the same things that you tell mount The first and second columns should be pretty straightforward.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
